| < Day Day Up > |
Direct addressing is a simple technique that works well when the universe U of keys is reasonably small. Suppose that an application needs a dynamic set in which each element has a key drawn from the universe U = {0, 1, ..., m - 1}, where m is not too large. We shall assume that no two elements have the same key.
To represent the dynamic set, we use an array, or direct-address table, denoted by T[0 ‥ m - 1], in which each position, or slot, corresponds to a key in the universe U . Figure 11.1 illustrates the approach; slot k points to an element in the set with key k. If the set contains no element with key k, then T[k] = NIL.
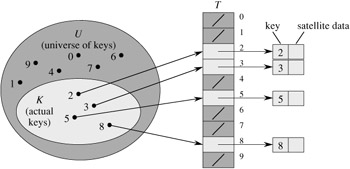
The dictionary operations are trivial to implement.
DIRECT-ADDRESS-SEARCH(T, k)
return T [k]
DIRECT-ADDRESS-INSERT(T, x)
T[key[x]] ← x
DIRECT-ADDRESS-DELETE(T, x)
T[key[x]] ← NIL
Each of these operations is fast: only O(1) time is required.
For some applications, the elements in the dynamic set can be stored in the direct-address table itself. That is, rather than storing an element's key and satellite data in an object external to the direct-address table, with a pointer from a slot in the table to the object, we can store the object in the slot itself, thus saving space. Moreover, it is often unnecessary to store the key field of the object, since if we have the index of an object in the table, we have its key. If keys are not stored, however, we must have some way to tell if the slot is empty.
Suppose that a dynamic set S is represented by a direct-address table T of length m. Describe a procedure that finds the maximum element of S. What is the worst-case performance of your procedure?
Suggest how to implement a direct-address table in which the keys of stored elements do not need to be distinct and the elements can have satellite data. All three dictionary operations (INSERT, DELETE, and SEARCH) should run in O(1) time. (Don't forget that DELETE takes as an argument a pointer to an object to be deleted, not a key.)
We wish to implement a dictionary by using direct addressing on a huge array. At the start, the array entries may contain garbage, and initializing the entire array is impractical because of its size. Describe a scheme for implementing a direct-address dictionary on a huge array. Each stored object should use O(1) space; the operations SEARCH, INSERT, and DELETE should take O(1) time each; and the initialization of the data structure should take O(1) time. (Hint: Use an additional stack, whose size is the number of keys actually stored in the dictionary, to help determine whether a given entry in the huge array is valid or not.)
| < Day Day Up > |